US EV ‘Battery Belt’ forming: battery cell production to exceed 900 GWh by 2030
US government has enacted both the Bipartisan Infrastructure Law and the Inflation Reduction Act (IRA), which not only aim to bolster the sales of electric vehicles but are also intended to decrease dependency on China’s EV battery supply chain.
Based on the car battery manufacturers’ strategies, it is anticipated that a “battery belt” will emerge, centered around traditional automotive industry clusters on American soil. Projections suggest that by the year 2030, the country’s battery cell production capacity will surpass 900 GWh, enough to power approximately 12 million electric passenger vehicles.
The EV supply chain comprises mineral extraction, refining and processing, battery material production, and battery cell manufacturing. While China lacks a significant advantage in critical mineral resources for batteries, it dominates over half of the global production capacity in mineral refining and battery manufacturing. In 2022, the United States only contributed 6% to the global battery cell production capacity, and its share in mineral refining and processing was around 1%.
With the gradual increase in EV sales in the US, there is a risk of heavy reliance on overseas, particularly Chinese, battery supply if a local battery supply chain is not concurrently established and production capacity is not expanded.
According to analyst Evan Chen from DIGITIMES Research, IRA provides car buyers with tax credits when purchasing EV produced or assembled in North America. Moreover, the act extends tax incentives to battery companies that establish manufacturing facilities in the US, including Tesla and its battery partner Panasonic. It is projected that these companies could receive a tax credit of around $1.8 billion in 2023. Automakers eligible for these tax incentives are anticipated to lower the prices of EVs in the US market, ultimately contributing to an overall surge in EVs sales.
US battery cell production capacity above 50GWh by 2030
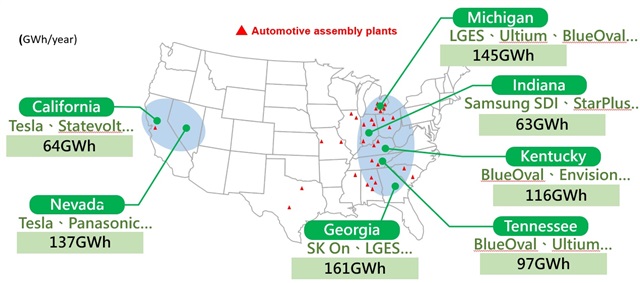
Source:Jay Turner, Wellesley College, covered companies, US Department of Energy, DIGITIMES Research, Jul 2023
Since the IRA passed, the investment in the US automotive battery and EV sector has soared to $60.2 billion. Remarkably, nearly 90% of this investment is directed towards battery production, indicating the compelling impact of the US government’s policies on the battery supply chain. Seven states in the US are projected to achieve annual battery production capacities exceeding 50 GWh, with particular emphasis on the traditional motor industry hubs connecting Michigan and Georgia, forming a burgeoning EV battery belt. However, during the transition to EV, the structural problems also put the job losses in the spotlight.
Within this battery belt, several battery plants can be found, such as Ford’s BlueOval battery park, operating as a joint venture with SK On, General Motors and LG Energy Solution’s formed Ultium Cells, and Stellantis expanded StarPlus Energy joint venture with Samsung SDI. The three major South Korean battery manufacturers have also established their respective production lines within this battery belt. Meanwhile, on the US west coast, California and Nevada primarily revolve around Tesla’s dominant battery supply chain.
About the analyst
Evan Chen holds a master’s degree in library and information science from National Taiwan University. His research focuses on autonomous driving technology, ride-hailing service/mobility as a service (MaaS), EVs and batteries.









