Enhancing Electronic Product Reliability: The Vital Role of Component Quality and Traceability
In the dynamic realm of electronics, the reliability of products is a cornerstone of consumer trust and industry reputation. This reliability is intricately linked to the quality and traceability of individual components used in electronic devices. A recent in-depth study has brought to light the significant impact that component degradation can have on electronic products’ Mean Time Between Failures (MTBF). This revelation underscores the critical need for quality control and comprehensive traceability in the electronics manufacturing process.
Decoding the Impact of Component Degradation
Electronic devices often have their reliability overlooked until a failure occurs. The study highlights that components compromised by factors like corrosion or manufacturing flaws can drastically reduce the MTBF of electronic products. This decrease in reliability leads to more frequent product failures, contributing to a surge in electronic waste and CO2 emissions. These environmental concerns are becoming increasingly pressing, necessitating a reevaluation of component quality and lifecycle management in electronic manufacturing.
The Crucial Role of Component Traceability and Quality
The concept of “component traceability” is pivotal in addressing these challenges. By meticulously tracking each component from its origin through the production and assembly process, manufacturers can ensure the integration of only the highest quality parts in their products. This level of traceability is essential for identifying and eliminating degraded components that could undermine the reliability of the final product. Similarly, “electronic component quality” is a critical determinant in the longevity and dependability of electronic devices. The study emphasizes the necessity for thorough and advanced inspection methods capable of assessing the quality of components at a granular level. Emerging technologies, such as artificial intelligence (AI) and big data analytics, are proving invaluable in this regard, offering the ability to detect defects that traditional inspection techniques might miss.
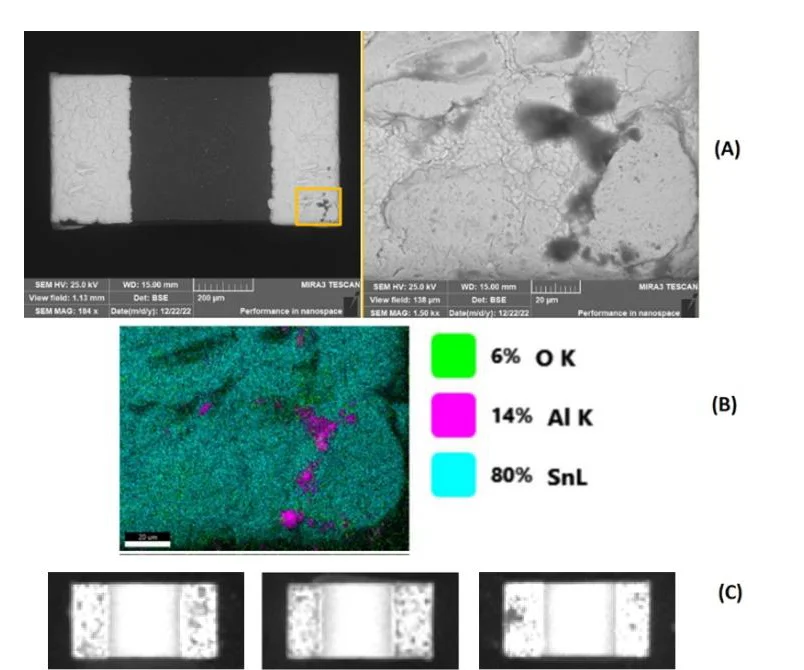
Real-World Implications and Economic Considerations
The practical implications of using subpar components are far-reaching. For example, including even a single degraded component can significantly elevate the failure rate of an electronic product. This increase in failures leads to higher costs associated with product returns and recalls, impacting the economic viability of electronic manufacturing. From a financial perspective, ensuring high component quality can lead to substantial cost savings. Furthermore, by enhancing the lifespan of electronic products, manufacturers can also reduce their environmental impact, cutting down on electronic waste and CO2 emissions.
Innovative Solutions for Improved Product Reliability
The study introduces cutting-edge solutions aimed at boosting the reliability of electronic products. One notable solution is integrating AI-driven inspection systems into the assembly lines. These systems are designed to detect visual anomalies, signs of corrosion, and other indicators of component degradation in real-time. By identifying these issues early in the production process, manufacturers can significantly improve their products’ overall quality and reliability. This proactive approach to quality control enhances product performance and contributes to building consumer trust and brand reputation in the competitive electronics market.
Conclusion: A Strategic Imperative for the Electronics Industry
The findings from this study serve as a strategic imperative for the electronics industry. A renewed focus on component traceability and quality is essential to ensure the long-term reliability and sustainability of electronic products. Adopting advanced inspection systems and leveraging the latest technological innovations will not only elevate product reliability but also lead to economic benefits and environmental conservation. As the electronics industry continues to grow and evolve, prioritizing these key aspects will be crucial in meeting the evolving demands of consumers and addressing global environmental challenges.











